Geographics in marketing is all about segmenting your audience based on where they physically are—from their country right down to their neighborhood. This works because, let's face it, where people live has a huge impact on their needs, culture, and what they buy. Tapping into these differences lets marketers deliver ads that actually resonate instead of falling flat.
Why Geographics in Marketing Matter More Than Ever
Picture this: you decide to open a high-end ski shop in the middle of Miami. It sounds completely absurd, doesn't it? That same logic applies to your digital ads. Blasting a generic, one-size-fits-all message to everyone, everywhere is like trying to sell snowboards on a tropical beach—it’s a massive waste of time and money because it ignores the basic context of your audience.
This is where geographics in marketing becomes a core part of your strategy, not just some dry textbook definition. It’s built on a simple but powerful truth: geography shapes everything. It influences local culture, language, climate, the economy, and even daily routines. All these factors directly steer consumer behavior, making location a powerful tool for connecting with people on their own terms.
The Foundation of Relevance and Efficiency
At its heart, geographic segmentation is about sending the right message to the right place. This isn't just a small tweak; it's the bedrock of any efficient, high-performing campaign. By focusing your budget on the areas where your ideal customers actually live, work, and shop, you immediately start to see a better return on ad spend (ROAS).
The whole idea is to stop wasting money talking to people who can't or won't buy from you. A local coffee shop in Portland, Oregon, has zero reason to serve ads to someone in Portland, Maine. Geographic targeting makes that crucial distinction possible.
This approach is more critical now than ever before. The global location-based advertising market flew past USD 81.7 billion in 2022 and is set to keep climbing as we all become more attached to our phones. With nearly everyone carrying a location-aware device, the ability to hit them with a timely, relevant offer based on their location is a massive competitive advantage.
From Broad Strokes to Hyper-Local Precision
Getting good at geographics in marketing means understanding all the different layers of targeting you can use. You can go big and target an entire country, or you can zoom in with surgical precision.
To make sense of it all, here's a quick breakdown of the key levels you'll be working with.
Key Levels of Geographic Segmentation
| Segmentation Level | Description | Best Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|
| Country | Targeting an entire nation. Best for managing international launches and navigating different laws or cultures. | A global streaming service promoting a new show release across North America. |
| Region / State | Focusing on a specific region, province, or state. Great for tailoring messages to regional climates or dialects. | A clothing brand advertising winter coats in the Northeast vs. swimwear in the Southwest. |
| City / DMA | Targeting a specific city or Designated Market Area (DMA). Aligns with local media markets, events, and urban trends. | A concert promoter running ads in the Nashville DMA for an upcoming country music festival. |
| ZIP Code / Radius | The most granular level, targeting specific postal codes or a radius around a point. Perfect for driving foot traffic. | A new restaurant sending a "grand opening" offer to everyone within a 2-mile radius. |
Learning how to stack and apply these different layers is a non-negotiable skill for any modern marketer. It’s a fundamental piece of effective social media ad targeting and your most direct path to boosting engagement and getting real results.
The Five Tiers of Geographic Ad Targeting
Knowing the theory behind geographics is one thing, but putting it into practice is where you really start to see results. Digital ad platforms give you a powerful set of tools to slice up your audience with incredible precision.
Think of it like a set of nesting dolls—each layer of targeting fits inside the last. You can go from a massive global audience right down to a single neighborhood block.
The right tier for your campaign comes down to your business goals, budget, and who you’re actually trying to reach. A multinational corporation launching a new app will play the game very differently than a local bakery promoting a weekend special. Mastering these five tiers is the key to spending your ad dollars wisely and making sure your message lands in front of the right people, in the right place.
This diagram breaks down how the different levels of geo-targeting stack up, moving from a broad, global focus to a hyper-local one.
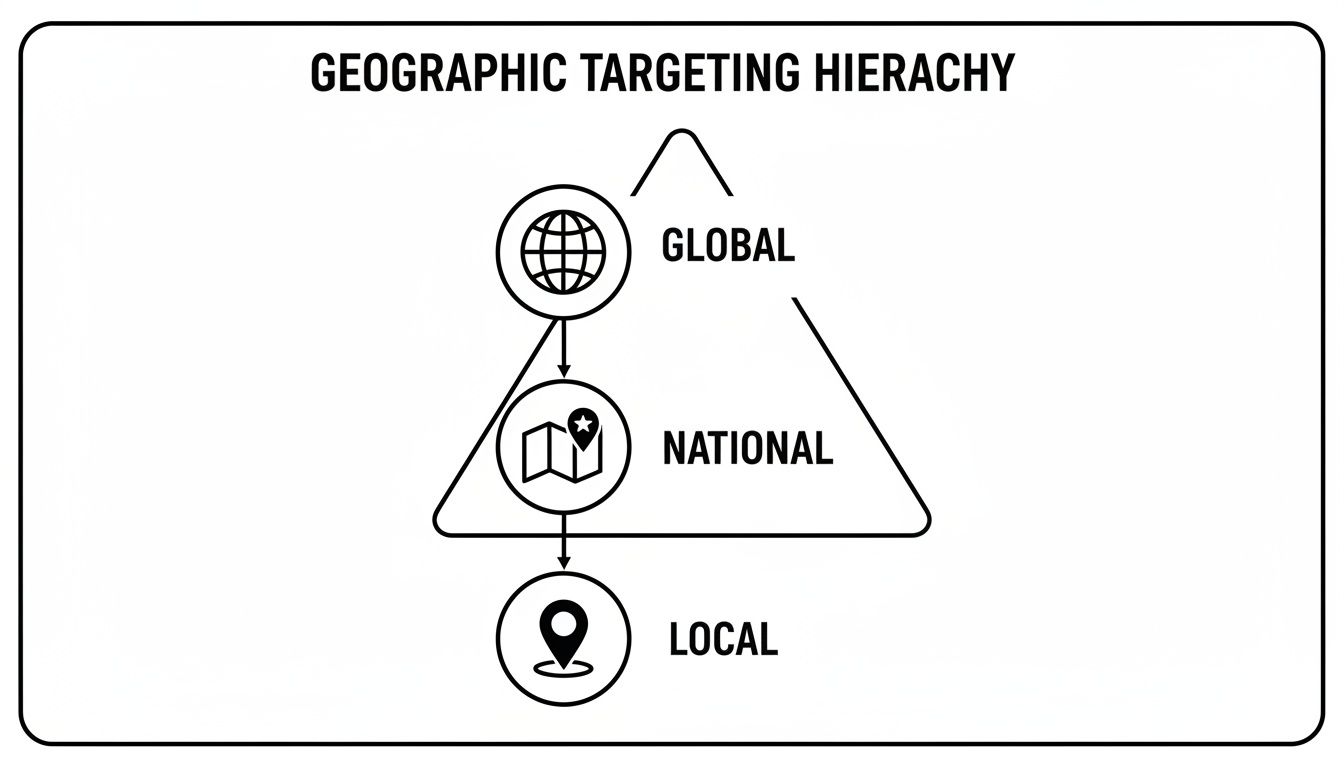
As you can see, each level offers a different trade-off between massive reach and pinpoint relevance. Let's break down when and why you'd use each one.
Tier 1: Country-Level Targeting
The widest net you can cast is country-level targeting. This is your go-to when you're running international campaigns, launching a product in several nations at once, or just need to manage brand messaging where different laws, cultures, or languages are a factor.
For example, a SaaS company rolling out a new feature might run totally separate campaigns for the United States, Germany, and Japan. This lets them translate ad copy, show pricing in local currencies, and schedule ads to run during each country's prime business hours. It's a simple move that prevents you from making the costly mistake of showing a US-centric ad to a European audience.
Tier 2: Region or State Targeting
Zooming in a bit, we get to region or state targeting. This is perfect for businesses whose products or services are tied to regional factors like climate, local culture, or specific regulations. It lets you craft more nuanced campaigns that speak directly to the shared experience of people in that specific area.
Think about a national clothing retailer. They could use state-level targeting to push heavy winter coats in Minnesota and Wisconsin while running ads for shorts and swimwear in Florida and Arizona. This simple segmentation makes the ads instantly relevant to the local weather, which can dramatically boost engagement and sales.
Tier 3: City-Level Targeting
City-level targeting gives you a much more concentrated focus. It’s ideal for promoting events, zeroing in on dense urban centers, or hitting areas packed with your ideal customers. Cities often have their own unique identities and competitive dynamics you can play to your advantage.
A national concert promoter, for instance, would absolutely use city-level targeting to sell tickets for a tour. Ads for a show in Denver would only be shown to people in and around that city, creating a super-focused campaign that doesn't waste a dime reaching people hundreds of miles away.
Key Takeaway: The goal of geographic targeting is to match your ad's reach to your business's operational footprint. Don't pay to show your ad to someone you can't serve. This principle becomes even more critical as you move down to the more localized tiers.
Tier 4: Designated Market Area (DMA) Targeting
A Designated Market Area (DMA) is a specific region in the U.S. where the local population gets the same TV and radio broadcasts. This is a powerful, and often overlooked, targeting tier that helps you sync up your digital campaigns with your traditional media buys.
If your company is running local TV spots in the Boston DMA, you can set your social media ads to target that exact same geographic footprint. This creates a powerful omnichannel effect, reinforcing your message across multiple channels and driving up brand recall with that local audience. Think of DMAs as the bridge between your online and offline advertising.
Tier 5: Radius and ZIP Code Targeting
Finally, we get to the most granular level: radius and ZIP code targeting. This is the bread and butter for any local business trying to drive foot traffic—restaurants, retail shops, gyms, you name it. It lets you draw a virtual fence around your location and serve ads only to people within that specific area.
A new pizza shop could target everyone within a 3-mile radius with a grand opening special. A real estate agent could target a few high-value ZIP codes to promote a new luxury listing. This hyper-local approach ensures every single ad dollar is spent reaching potential customers who can physically walk through your door.
To get the most out of these local tiers, it helps to pair them with proven local marketing strategies that can seriously amplify your efforts.
How to Localize Your Creative and Messaging

Simply targeting an area on a map is only half the job. If your message doesn't genuinely connect with the local culture, you might as well be shouting into the void. This is where great localization comes in. It’s about being a cultural translator for your brand, proving to customers that you see their world, not just their zip code.
This means ditching the generic, one-size-fits-all ad copy. The goal is to craft messages that feel like they were made just for the person seeing them. When you nail this, your ads stop feeling like an interruption and start feeling like a relevant conversation.
And the numbers don't lie. The market for location-based marketing has absolutely exploded, growing from USD 33.4 billion in 2020 to USD 59.7 billion in 2023. A staggering nine out of ten marketers say it drives more sales, and 86% see a bigger customer base. It’s clear: a local touch pays off.
Acting as a Cultural Translator
True localization runs much deeper than just dropping a city name into a headline. It’s about digging in and understanding the unique quirks and nuances of an area. This is how you build a connection that a generic national campaign could only dream of.
Here are a few ways to make your creative feel authentically local:
- Speak Their Language: We’re not just talking about Spanish vs. English. Use the slang, idioms, or pronunciations people in that area actually use. A campaign in New Orleans could mention "lagniappe" (a little something extra), while a Pittsburgh ad might talk about someone being "nebby."
- Use Local Landmarks: Feature beloved local spots in your visuals. An ad for running shoes in Austin could show someone on the trail at Zilker Park. For residents, it’s an instant, subconscious nod that says, "we get you."
- Reflect the Community: Use models and actors in your ads who actually look like the people who live there. Representation matters, and showing you understand the diversity of a community builds immediate trust and relatability.
Aligning Promotions with Local Context
Beyond the look and feel, your offers need to make sense locally. Context is everything. A promotion that’s a home run in one city could be a total dud in another, even if they're in the same state.
Think about these contextual triggers:
- Weather Patterns: A coffee chain could run ads for iced lattes in Phoenix during a heatwave while pushing hot mochas in a rainy Seattle. It’s a simple tweak that makes the offer feel incredibly timely and intuitive.
- Local Events and Teams: Tap into local pride by aligning your promotions with major events, festivals, or sports. A Chicago business running a "game day" special when the Bears are playing is connecting with the city's energy and excitement.
Key Insight: Localization isn’t just about making your ad look local. It’s about making your offer feel indispensable to that specific audience, at that specific moment. That’s how you turn geographic data into a real reason to buy.
Scaling Localization with Technology
Okay, so manually creating unique ad variations for every single city or DMA sounds like a logistical nightmare, right? For a long time, it was. This was the biggest hurdle for brands—it was just too time-consuming and expensive to do localization right.
This is where automation and AI change the game. Modern platforms like AdStellar AI were built to solve this exact problem. Instead of painstakingly building every ad one by one, you can generate hundreds of geo-specific variations in minutes.
Imagine you're a national retailer. With an AI tool, you can upload a core creative concept and instantly spin up versions for your top 50 markets. Each one could feature a different local landmark, a headline calling out the city, and copy tweaked for local flavor. A huge part of this is writing copy that connects, so check out our guide on how to write good ad copy for more on that.
By automating the creation and testing of these variants, localization transforms from a creative nice-to-have into a measurable performance strategy. You can quickly see which images, messages, and offers resonate in which locations, then pour your budget into the winners. This turns your geographics in marketing strategy from a simple targeting tactic into a scalable engine for growth.
Measuring and Optimizing Geographic Campaigns
Great marketers don't guess—they measure. Once your campaigns with localized creative are live, the real work begins. The goal is to ditch assumptions and use hard data to find those hidden pockets of profitability, trim wasted ad spend, and double down on the locations that actually drive results.
This means you need to track the right metrics. Instead of just looking at performance on a national level, you have to break it down geographically. This shift in perspective often uncovers surprising insights, like a city with a high Cost Per Click (CPC) that also happens to deliver your most valuable customers.
Establishing Your Core Geographic KPIs
To really understand what’s working, you need to go beyond surface-level data. While your ad platform’s dashboard is a decent starting point, the true gold is found by tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) at each geographic level you’re targeting.
Here are the essential metrics to keep an eye on:
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) by City/Region: This tells you exactly how much it costs to land a new customer in different locations. You might find your CPA in Austin is half of what it is in Dallas, which is a clear signal to reallocate your budget.
- Return On Ad Spend (ROAS) by State/DMA: This is the ultimate measure of profitability. Tracking ROAS by geographic area shows you precisely where your ad spend is generating the most revenue, helping you identify your most valuable markets.
- Conversion Rate (CVR) by ZIP Code: For local businesses, this metric is everything. It reveals which specific neighborhoods are most responsive to your offers, allowing for truly hyper-local optimization.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) by Region: This is a more advanced metric, but it’s incredibly powerful. It helps you understand if certain areas produce higher-value, long-term customers, which can justify a higher initial CPA.
Analyzing these KPIs helps you build a performance map of your target areas. It shows you where to scale up, where to pull back, and where to test new messaging. For a deeper dive into the most important profitability metric, our guide on how to calculate Return On Ad Spend provides a detailed walkthrough.
Designing a Simple Geographic A/B Test
Data analysis tells you what happened in the past, but A/B testing tells you what could happen next. Running simple geographic tests is the single best way to validate your localization hypotheses and find winning creative combinations. The idea is to isolate one variable—like a localized ad—and see how it impacts performance in a specific area compared to a control.
A classic example is testing a generic national ad against a version specifically localized for the Chicago DMA. This allows you to measure the real-world lift of your localization efforts, proving (or disproving) your assumptions with data.
The global geomarketing market hit USD 17.77 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a blistering 23.1% CAGR through 2030, largely thanks to smartphones. For marketers, tools like geofencing—which now makes up around 30% of the location-based ad market—can boost foot traffic by up to 200% by creating virtual boundaries around key locations.
To help you get started, here's a simple framework for structuring your geo-based tests.
Geographic A/B Test Design Template
| Test Element | Control Group (Group A) | Variable Group (Group B) | Primary KPI to Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ad Creative | Generic national ad copy and image | Ad copy and image referencing local landmarks or slang | Conversion Rate or ROAS |
| Offer | Standard 10% off promotion | Special offer exclusive to a specific state (e.g., "Texas-sized discount") | CPA or Conversion Rate |
| Landing Page | General company landing page | Landing page with local testimonials and imagery | Lead Form Submissions |
| Audience | Broad regional targeting (e.g., entire Northeast) | Hyper-local targeting (e.g., specific ZIP codes in Boston) | ROAS or CPA |
This structure helps ensure you're testing one thing at a time, giving you clean data to make a clear decision on what works best and where.
Using AI to Uncover Hidden Insights
Manually crunching performance data for dozens—or even hundreds—of locations is a nightmare. Spreadsheets quickly become a tangled mess, making it almost impossible to spot subtle trends or identify the true drivers of performance. It’s tedious and wide open to human error.
This is where AI-powered tools come in and change the game.
Platforms like AdStellar AI connect directly to your ad accounts and automate this entire process. The technology can instantly analyze performance across all your geo-audiences, pinpointing your top-performing cities, states, and DMAs without any of the manual grunt work.
Even more importantly, these systems can analyze creative elements alongside geographic data. AI can highlight which images, headlines, or calls-to-action resonate most strongly in specific regions. This moves you from raw data to actionable insights, empowering you to make smarter, faster decisions to optimize your geographics in marketing.
Common Pitfalls and Privacy Considerations
Geographic targeting is an incredibly powerful tool, but it comes with a lot of responsibility. If you get it wrong, you’re not just looking at a wasted budget—you could alienate customers or even land in legal hot water. The trick is to walk the line carefully, treating both your ad spend and your customer’s data with the respect they deserve.
One of the most common traps marketers fall into is over-segmentation. It’s tempting to slice your audience into dozens of hyper-specific micro-locations, but this almost always backfires. When your segments are too tiny, ad platforms can’t gather enough data to properly optimize, leaving you with erratic performance and unpredictable results.
Another big one is leaning on lazy stereotypes instead of actual data. Assuming everyone in a wealthy ZIP code is shopping for luxury goods, or that a rural town isn’t tech-savvy, is a recipe for disaster. These generalizations don’t just miss the mark; they can make your brand look clueless and out of touch.
Avoiding Common Geographic Mistakes
To keep your campaigns sharp, effective, and respectful, make sure you sidestep these frequent errors:
- Ignoring Regional Nuances: A campaign that kills it in California might completely flop in Texas due to cultural or even regulatory differences. It’s easy to forget just how different local rules can be. For example, some products face specific county-level shipping restrictions that go beyond statewide laws, a detail that can cause major headaches if overlooked.
- Setting Unrealistic Radii: If you’re a local coffee shop targeting a 20-mile radius, you're probably burning cash on people who will never visit. Think realistically about how far a customer will actually travel for what you offer and set your radius accordingly.
- Forgetting to Exclude Locations: This one is simple but so often missed. Always exclude areas where you don’t ship, have no physical presence, or where campaigns have consistently underperformed. It’s an instant way to make your budget work harder.
Navigating the World of Data Privacy
Beyond campaign tactics, the single most critical piece of the puzzle is privacy. People are smarter and more protective of their data than ever before, and regulations like Europe's GDPR and California's CCPA have put serious legal weight behind that sentiment.
These laws aren't just red tape. They’re a clear signal from consumers and governments that you need to be transparent and responsible with location data. Failing to comply can lead to staggering fines, but the real cost is the catastrophic loss of customer trust—something that’s nearly impossible to win back.
Think of privacy compliance not as a limitation, but as a competitive advantage. Brands that are transparent about the data they collect and why they collect it build stronger, more loyal relationships with their customers. Trust is the ultimate currency.
Using geographic data responsibly is all about leading with value and transparency. Your privacy policy should clearly explain how you use location data to create better, more relevant experiences—not to just follow people around the internet. As third-party cookies fade away, ethically managing your first-party data has become absolutely essential. To get a better handle on this shift, check out our guide on the future of third-party data.
When you adopt a privacy-first mindset, you move from a purely transactional relationship to one built on mutual respect. This approach doesn't just keep you out of trouble; it builds a stronger brand and fosters the kind of loyalty that sustainable growth is made of.
Scaling Your Location Strategy with AI
So you've nailed down the strategy, figured out the creative angles, and know how you'll measure success. Now for the hard part: how do you actually do all of this without completely burning out your team? The reality of geographic marketing is that managing hundreds of campaigns for different locations can quickly spiral into an operational mess.
This is where you turn theory into a scalable growth engine. Modern AI platforms are the force multiplier you need, automating the entire workflow from creating the ads to optimizing them on the fly. They solve the biggest headache of a complex location strategy: getting it done without drowning in manual, repetitive tasks.
From Hours of Tedious Setup to Minutes of Creation
Think about the old way of launching localized campaigns. You’d sit there, painstakingly duplicating ad sets, swapping out an image for Dallas, then another for Denver, and tweaking headlines for every single market. It wasn't just slow—it was a recipe for mistakes, making it nearly impossible to manage more than a few locations well.
AI-driven tools flip that entire process on its head.
Instead of duplicating campaigns one by one, you can now generate thousands of localized ad variants in minutes. This is how you unlock true scale.
An AI platform can take a single creative idea and instantly spin up versions for every major DMA, complete with unique local imagery and copy. This frees up your team from the mind-numbing grunt work of campaign setup. They can finally focus on what matters: analyzing performance, spotting new market opportunities, and coming up with the next great creative concept.
Intelligent Optimization That Finds the Winners for You
Launching all those ad variations is just step one. The real magic begins when the AI starts crunching the performance data as it rolls in. It connects the dots between creative, audience, and location to automatically find your winning combinations.
- Creative Analysis: The AI can figure out which images or videos perform best in certain regions. It might discover that lifestyle photos get a lower CPA in the Midwest, while product-focused creative crushes it on the East Coast.
- Audience Identification: The system pinpoints which geo-targeted audiences are delivering the best ROAS, giving you the confidence to shift your budget toward the most profitable markets.
- Automated Scaling: Once a winning ad in a specific location is identified, the AI can automatically push more budget behind it. No more checking dashboards every hour to make sure you're capitalizing on what's working.
This continuous learning loop turns campaign management from a reactive chore into a proactive strategy. Platforms like AdStellar AI handle this entire workflow, helping teams get a deeper understanding of AI for Facebook Ads and how automation delivers better results. By letting the technology find and scale your winners, you can build a far more efficient and profitable advertising machine.
Frequently Asked Questions About Geographics in Marketing
Even with a solid game plan, questions always pop up when you start putting geographic targeting into practice. Let's tackle some of the most common hurdles marketers run into, giving you clear, straightforward answers to move forward with confidence.
How Do I Know Which Level of Geographic Targeting Is Right for Me?
The right level comes down to your business model and what you're trying to achieve with a specific campaign. An e-commerce brand that ships nationwide can start broad—think country or state level—and then use performance data to drill down into the regions that are actually driving sales.
On the other hand, a local service business, retailer, or restaurant needs to be much more precise. For them, spending ad dollars on anyone outside a specific radius or ZIP code is a waste. They need to reach customers they can physically serve. The key is to match your geographic scope to your operational footprint, then let the data (like CPA or ROAS) tell you where to tighten the focus.
Can I Combine Geographic Targeting with Other Audience Types?
Absolutely, and you definitely should. This is called audience layering, and it’s how you go from a broad audience to a highly specific and effective one. When you combine location with other data points, you filter out irrelevant people and make your ad spend work much harder.
For example, on a platform like Meta, you could target users who are:
- Within a 10-mile radius of your new gym (Geographic)
- Aged 25-45 (Demographic)
- Interested in "fitness" and "healthy eating" (Interests)
This layered approach creates a much more relevant audience than using any single attribute alone, which dramatically increases the odds of someone taking action.
By layering targeting criteria, you move from simply finding people in a location to finding your ideal customer within that location.
What Is the Difference Between Geofencing and Geotargeting?
It's a subtle but important distinction. Think of geotargeting as setting the overall stage for your campaign, while geofencing is a specific, real-time action happening on that stage.
Geotargeting is the broader practice. It’s when you deliver ads to a predefined geographic area, like targeting everyone in the city of Chicago for an entire campaign. It’s a static boundary you set and forget.
Geofencing, however, is much more dynamic. It involves setting up a virtual boundary around a smaller, very specific location—like a competitor’s store, a trade show, or a concert venue. An ad or notification gets triggered the moment a user’s device enters or exits that precise boundary. Geofencing is a powerful tactic for hyper-local marketing designed to drive immediate action.
Ready to stop manually building hundreds of localized ad variations? AdStellar AI automates the entire process, letting you launch, test, and scale geo-targeted campaigns 10x faster. Discover how AdStellar AI can transform your location strategy.



